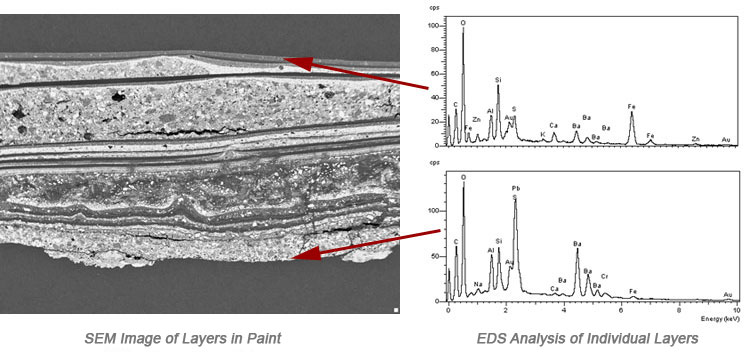
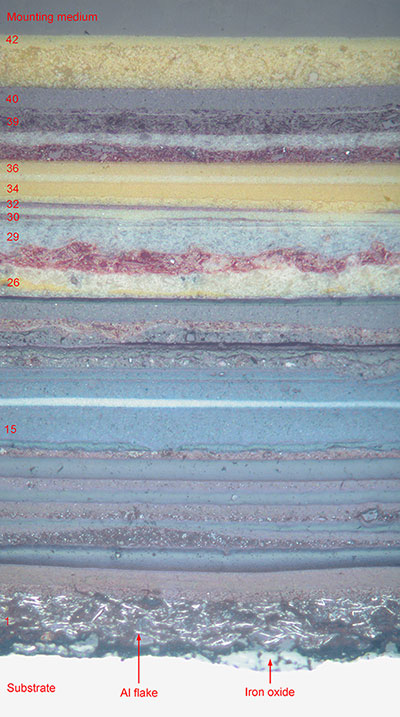
Paint Analysis
Investigation of paint by sectioning and examining in cross-section can allow details of individual layers to be identified, such as:
- Pigments
- Toxic elements
- Lead
- Cadmium
- Antimony
- Cobalt
- Arsenic
- Mercury
- Intumescent
- Glazing putty
Techniques including scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can be used to examine modern and historic samples of paint and polychrome. Inorganic fillers, pigments and organic constituents in the separate paint layers can be analysed and identified by energy dispersive x-ray analysis. The information provides a description of formulation and thickness of each layer. Dry-film thickness of paints and varnishes can be determined using ISO 2808.
Further examination techniques used to examine paint samples include optical microscopy and Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy to determine the polymeric components.
Other properties relevant to paint analysis are hardness and adhesion. Pendulum hardness can be used to determine paint hardness. Adhesion of coatings to metal substrates can be determined by applying and removing tape over cuts made in the film.