REFRACTIVE INDEX
Background
The refractive index of a transparent material is a fundamental of that material and can be used to identify the material. The ratio of the velocity of light in vacuum to the velocity of light in a medium is referred to as the refractive index of the medium, n.
If light travelling inside a material such as glass with a larger refractive index n2 than that of the material outside, n1, such as air, there is an angle, the critical angle of incidence, ic, beyond which the light is reflected back into the material and does not escape. This phenomenum is referred to as total internal reflection.
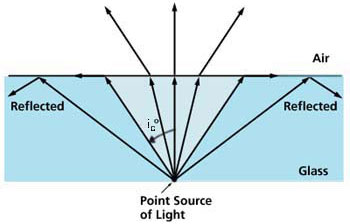
The critical angle is given by:
sin ic = n1 / n2
The Abbe refractometer is used to measure the refractive index of transparent solids using the critical angle effect. The sample should have at least one flat polished face. The sample size is ideally about 10 x 20 x 3mm but smaller samples can be used.

Bellingham and Stanley Abbe Refractometer
Standards
| ASTM D542-14 | Standard Test Method for Index of Refraction of Transparent Organic Plastics |
| ISO 489:1999 | Plastics -- Determination of refractive index |
| E1967-98(2003) | Standard Test Method for the Automated Determinaton of Refractive Index of Glass Samples Using the Oil Immersion Method and a Phase Contrast Microscope |